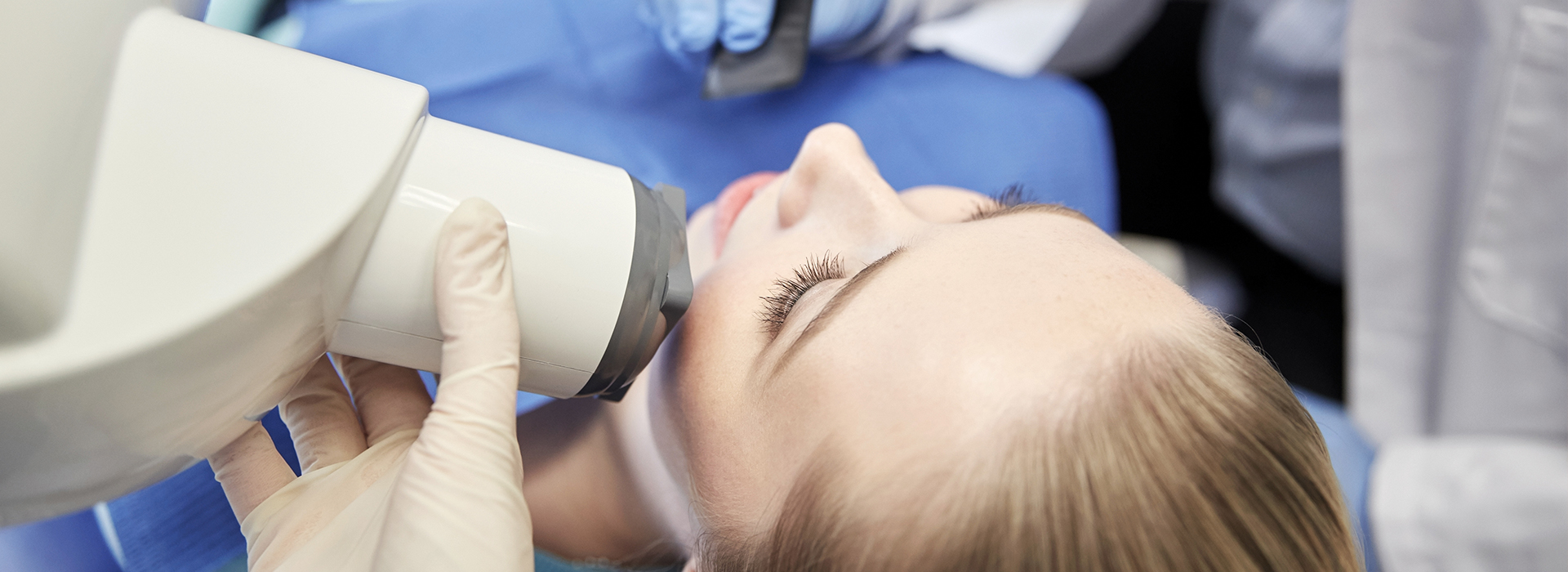
Digital radiography is the modern method of producing dental X-ray images using electronic sensors and computer processing instead of traditional film. The sensor captures the image as a digital file that appears on a monitor almost immediately, giving clinicians instant visual feedback. This speed transforms chairside conversations: images can be reviewed with patients in real time, annotated for clarity, and used to explain findings without delay.
Beyond convenience, digital radiography supports more consistent image quality. Digital files can be adjusted for contrast and brightness, cropped to highlight areas of concern, and enlarged without losing essential detail. Those capabilities help clinicians detect early signs of decay, bone changes, or other conditions that might be less obvious on conventional film.
For modern dental practices, adopting digital radiography is about improving diagnostic capability while streamlining workflow. It reduces wait times for image processing, decreases the chance of lost film, and integrates smoothly with digital patient records. Collectively, those benefits raise the standard of care and make visits more efficient for both the dental team and patients.
Digital sensors come in several styles, including intraoral plates and smaller sensors designed to fit comfortably in the mouth. When positioned behind the teeth, these devices register X-ray photons and convert them into an electronic signal. That signal is then translated into a high-resolution image by software, providing clear visualization of tooth structure, restorations, and supporting bone.
Unlike film, digital sensors do not require chemical processing. The moment the image is captured it appears on a screen, where it can be inspected at varying magnifications and analyzed using measurement tools. This immediacy supports more accurate treatment planning, because the clinician can confirm image quality and retake an image if necessary while the patient is still in the chair.
Sensor design has improved significantly over the years to prioritize patient comfort and image fidelity. Thin, flexible plates reduce gag reflex and positioning issues, while higher pixel density enhances the detection of subtle changes. These technical refinements make intraoral imaging a routine, dependable part of comprehensive dental care.
One of the most important advantages of digital radiography is its efficiency in using X-ray exposure. The sensors are more sensitive to X-rays than traditional film, which means diagnostic images can be produced with a much lower dose of radiation. Lower exposure is an important safety consideration for routine dental monitoring and for patients who require periodic imaging over time.
Digital systems also enable targeted imaging protocols: clinicians can capture smaller, focused images of specific teeth or areas rather than taking broad, higher-dose views unnecessarily. When combined with modern X-ray units that permit precise control over exposure settings, this targeted approach further minimizes cumulative radiation while preserving diagnostic value.
Practices that prioritize radiation safety follow established guidelines for when and how often images should be obtained. Digital radiography supports those protocols by delivering high-quality images at lower doses, making it a responsible choice for ongoing oral healthcare monitoring.
Digital images enhance diagnostic confidence by allowing clinicians to manipulate images in ways not possible with film. Brightness and contrast adjustments can reveal hidden decay, subtle fractures, or early bone loss; measurement tools provide accurate assessments of root length or bone height for restorative and surgical planning. These capabilities help clinicians create more precise, individualized treatment plans.
Another practical advantage is seamless integration with clinical software. Digital X-rays become part of the patient’s electronic health record where they can be compared side-by-side with previous images. This longitudinal view makes it easier to spot gradual changes and evaluate the effectiveness of treatments over time, strengthening preventive care and long-term outcomes.
Because images are available instantly, communication among dental team members is faster and clearer. Specialists, hygienists, and assistants can review the same digital files simultaneously, improving collaboration and speeding decision-making. That interoperability is particularly valuable when coordinating complex procedures such as implant placement or full-mouth rehabilitation.
Finally, the ability to annotate and export images supports patient education. Clinicians can illustrate specific concerns and proposed interventions directly on-screen, making it easier for patients to understand their condition and the rationale behind recommended care.
Digital files simplify the storage and retrieval of radiographs. Instead of physical film files that occupy space and require careful handling, digital images are archived within secure practice management systems. Efficient indexing and search functions make it straightforward to locate past images during follow-up visits, improving continuity of care and recordkeeping accuracy.
Sharing images with other providers is also more efficient with digital radiography. Electronic files can be transmitted securely to specialists or referring offices when collaboration is needed, eliminating the delays and logistical challenges of mailing physical film. Faster information exchange supports coordinated treatment and can reduce the need for duplicate imaging.
From an environmental standpoint, digital radiography eliminates the chemical processing used by traditional film, which reduces hazardous waste and chemical disposal concerns. The decrease in paper and film consumption is another sustainability benefit, aligning modern dental practice with environmentally responsible operations.
Together, these advantages—compact storage, secure sharing, and reduced environmental impact—make digital radiography a practical and forward-looking choice for delivering dependable dental care.
Digital radiography is a foundational technology that improves diagnostic clarity, enhances patient safety, and streamlines clinical workflow. When implemented thoughtfully, it supports better communication, more precise treatment planning, and responsible recordkeeping. If you’d like to learn more about how digital imaging is used in our office or how it can benefit your care, please contact us for additional information.
Digital radiography is the process of capturing dental X-ray images with electronic sensors and software instead of film. The sensor converts X-ray photons into an image file that appears on a monitor almost immediately, enabling faster clinical decisions. This shift from film to digital changes how clinicians review, annotate, and explain images during the visit.
Beyond speed, digital radiography improves image consistency because files can be adjusted for brightness, contrast, and magnification without losing essential detail. Those capabilities help identify early signs of decay, bone changes, and other conditions that might be less obvious on conventional film. Together, these benefits enhance diagnostic accuracy and streamline patient care.
Digital intraoral sensors come in several designs, such as thin plates and smaller rigid sensors, which are positioned inside the mouth to record X-ray photons. The sensor translates those photons into an electronic signal that imaging software converts into a high-resolution image for immediate review. This direct conversion eliminates chemical processing and reduces the chance of lost or damaged film.
Modern sensors are engineered for patient comfort and image fidelity, with thinner profiles and higher pixel density to reduce gag reflex and capture fine detail. Clinicians can inspect images at varying magnifications, take measurements, and retake images if necessary while the patient is still in the chair. These practical improvements support more reliable treatment planning and efficient appointments.
Digital X-ray sensors are more sensitive to X-rays than traditional film, which typically allows clinicians to use a much lower radiation dose to obtain diagnostic-quality images. Lower exposure is an important safety advantage, especially for patients who need periodic imaging as part of ongoing monitoring. Advances in sensor technology and exposure control have reduced cumulative dose without sacrificing diagnostic value.
In addition, digital systems support targeted imaging protocols that capture only the necessary area, avoiding broad high-dose exposures when they are not needed. Clinicians follow established safety principles, including careful case-by-case assessment of imaging needs and protective measures during capture. This combined approach helps minimize radiation while maintaining the ability to diagnose and treat effectively.
Digital images can be manipulated with tools that adjust contrast and brightness, reveal hidden decay, and highlight subtle fractures or bone loss. Measurement features allow precise assessment of root length, bone height, and restoration margins, which is especially useful for restorative and surgical planning. These image enhancements give clinicians better information to make informed, individualized treatment recommendations.
Digital radiographs integrate with electronic records so clinicians can compare current images with prior studies side by side, making it easier to track gradual changes over time. Faster sharing and simultaneous review among team members improve collaboration and speed decision-making for complex cases. The result is clearer communication, more confident diagnoses, and treatment plans tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
Yes, digital radiographs can be transmitted electronically to specialists, referring offices, or other members of the care team for consultation. Electronic files eliminate the delays and logistical challenges of mailing film and allow secure, encrypted transfer when appropriate. Faster information exchange supports coordinated treatment and reduces the likelihood of duplicate imaging.
The office of Christopher R. Szydelko, DDS PC uses digital workflows that make it straightforward to send images for second opinions or specialist planning when collaboration is needed. Patients may be asked to sign release forms consistent with privacy regulations before records are shared, and clinicians will explain the reason for any transfer. Efficient digital sharing improves continuity of care while protecting patient privacy.
During a digital radiography appointment, the clinician or assistant will position a small sensor or plate in the mouth and align the X-ray unit for a very brief exposure. The capture is fast, often completed in seconds, and the image appears on the monitor almost immediately for quality review. Patients may notice a slight pressure from the sensor but generally experience greater comfort than with older film holders.
After images are captured, the clinician will review them with the patient, explain any findings, and answer questions while the patient is still in the chair. Protective measures such as lead aprons are used as appropriate to minimize exposure, and clinicians will only recommend images that are diagnostically necessary. This immediate feedback helps patients understand their oral health and the rationale for recommended care.
Digital radiography complements other digital tools like intraoral cameras, digital impressions, and CAD/CAM systems to create a cohesive clinical workflow. Images can be combined with three-dimensional scans and intraoral photographs to plan restorative, orthodontic, or implant procedures more precisely. That multi-source data supports comprehensive treatment simulations and clearer patient communication.
For example, clinicians use digital radiographs alongside planning software to evaluate bone structure for implant placement or to verify tooth positions during aligner therapy. The interoperability of digital systems speeds collaboration between general dentists and specialists and enhances the predictability of complex treatments. Integrated imaging therefore helps deliver more accurate and efficient care.
Digital radiographs are archived within secure practice management systems or picture archiving and communication systems that index images for easy retrieval. Electronic storage reduces the need for physical film files and enables rapid access to prior images during follow-up visits. Proper indexing and backup routines ensure continuity of records and protect clinical data from accidental loss.
Access to stored images is controlled through user permissions and secure login protocols to protect patient privacy and comply with applicable regulations. Regular backups and encrypted transmission help maintain data integrity and confidentiality when images are shared with other providers. These safeguards make digital storage both practical and responsible for long-term recordkeeping.
Digital radiography eliminates the chemical processing required for traditional film, removing a source of hazardous waste and reducing the need for chemical disposal. By avoiding film and processing chemicals, practices reduce their environmental footprint and the risks associated with handling and disposing of those materials. The absence of film also reduces paper use for labeling and storage associated with physical records.
Additionally, digital files require less physical storage space and fewer resources for record management, supporting more sustainable office operations. When combined with secure electronic sharing, digital radiography reduces the need for duplicate images and physical transport, which further decreases environmental impact. These factors make digital imaging a greener choice for modern dental care.
Frequency of radiographic imaging is determined on an individual basis by the clinician after evaluating your oral health history, risk factors, and current clinical findings. Professional guidelines inform these decisions, but the final recommendation is personalized to balance diagnostic benefit with radiation safety. Clinicians consider factors such as caries risk, periodontal condition, and previous treatment when planning imaging intervals.
Your dental team will discuss the rationale for any recommended images and answer questions about the type and timing of radiographs. Christopher R. Szydelko, DDS PC follows best-practice principles to use the lowest exposure necessary while obtaining the information needed for diagnosis and treatment planning. Open communication ensures patients understand why images are requested and how they contribute to effective care.
